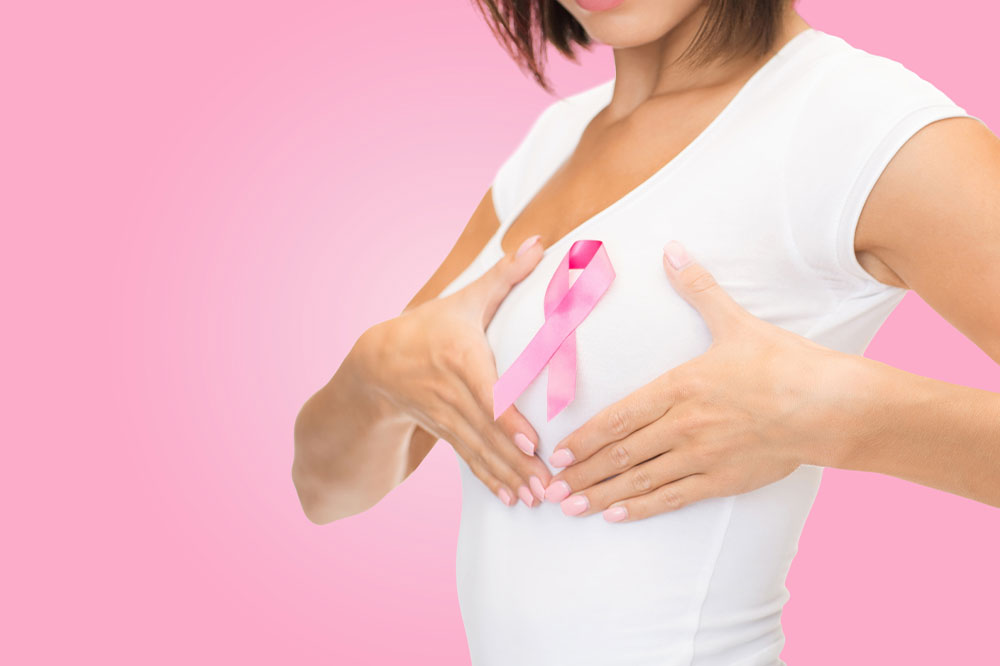
Breast Cancer – Symptoms, Stages, and Risk Factors
Breast cancer occurs when cancerous cells grow and spread uncontrollably, leading to a tumor that can also spread to other parts of the body. The risk of developing breast cancer depends on several factors, and the condition manifests in various ways. So, it’s important to understand the symptoms, stages, and risk factors of breast cancer to facilitate early diagnosis and timely treatment.
1. What are the symptoms of breast cancer?
Different types of breast cancer have varying symptoms, and some patients may not showcase any symptoms. When they do, the following are some of the common signs:
- A painless lump is an early common sign of breast cancer. That said, the tumors are as small as a pea and unnoticeable to the naked eye sometimes, so it is important to get timely mammograms for the detection of tumors.
- Breast cancer can lead to changes in the size, shape, and contour of the breasts.
- Some patients may also notice a blood-stained or clear discharge.
- The skin near the breast or nipple feels scaly, inflamed, or puckered. It can also exhibit redness and pain.
2. What are the stages of breast cancer?
Breast cancer has five stages:
- Stage 0 is also called carcinoma in situ. This is the stage wherein the tumor cells are contained to one part of the breasts.
- Stage I is the earliest stage of invasive breast cancer. Cancerous cells have grown but haven’t reached any lymph nodes at this stage, and the tumor measures around 2 cm.
- At stage II, the cancerous tumors measure between 2 to 5 cm, and the cells have spread to the surrounding breast tissue.
- Stage III breast cancer is characterized by tumors that are over 2 inches in diameter. Cancer has spread to the underarm lymph nodes or other surrounding tissues.
- Stage IV or metastatic breast cancer refers to the cancerous growth spreading to near or distant body parts. The affected areas may include bones, brain, lungs, or liver.
3. What are the common risk factors for breast cancer?
Some risk factors of breast cancer can be managed, while some others cannot be controlled. Here are a few common factors that elevate the risk of this disease:
- Gender and increasing age
Women above 55 are more likely to develop breast cancer. - Family history
Age and gender, coupled with a family history of the disease, make an individual a high-risk patient. About 10 percent of breast cancer cases are inherited. - Race
White women, Asian or pacific islander women, and Hispanic or Latina women are at high risk of developing breast cancer.
Other risk factors include lifestyle choices. Excessive alcohol consumption (more than one alcoholic beverage per day) increases the risk of developing this condition by 20 percent. Obesity and leading a sedentary lifestyle are best avoided to limit the risk of breast cancer.